EMR Integration

Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
Technology Overview and Workflow Planning Guide
NPi® Pupillometer System Integration Overview

The NPi-200 and NPi-300 Pupillometers are point-of-care devices, however the pupillometers do not facilitate transmission of patient data into an EMR, are not connected to an EMR, and will not be connected to your hospital’s network. The patient information (pupil measurement data) is contained on the patient-specific disposable SmartGuard® product that has an embedded RFID smart card memory tag.
The patient data on the SmartGuard is not able to be exported in HL7 protocol. As with all other point-of-care devices (ie: ventilators, glucometers, etc.) whose biometric feeds or patient data must be converted into HL7, the patient’s pupil measurements contained on the SmartGuard must also be converted into HL7 to upload into your EMR. To facilitate transmission of the patient data on the disposable SmartGuard into any EMR system, it will require a device driver provided by a third party (ie: Capsule Technologies, iSirona/Nanthealth, Cerner, etc.) of which will be specified by you and your IT department. Note that both the NPi-200 and NPi-300 Pupillometers use the same SmartGuard, thus the information here applies to both Pupillometers.
Our Technology
The NPi Pupillometer uses RFID (radio frequency identification) technology to transfer data between the NPi Pupillometer and the SmartGuard®. RFID facilitates data collection at high speed using low wattage (13.56 MHz) radio frequency to read from and write to the SmartGuard memory. Incorporated into the design of the NPi Pupillometer is a radio frequency (RF) antenna which broadcasts patient data information to the SmartGuard.
SmartGuard®
The disposable SmartGuard incorporates a 4K RFID technology manufactured by Mifare. The memory consists of a sequence of blocks each containing a pair of measurements from the left and right eye. Each pair is time-stamped and contains the pupillary variables from both the left and right eyes. The Mifare 4K memory can store up to 168 paired measurements. Data saved in the memory can be accessed using a RFID reader device (SmartGuard Reader).
Entering the Patient Identification Number

To program a new SmartGuard, attach a SmartGuard to the NPi Pupillometer. Enter the patient identification (ID) number either by manual entry or by using the NPi-300 Incorporated Barcode Scanner. If using the scanner, scan the barcode printed on the patient’s wristband to write the patient ID into both the NPi Pupillometer and the SmartGuard memory. Every valid pupillary measurement will be saved into the SmartGuard memory. The NPi-300 Pupillometer contains an Incorporated Barcode Scanner for easy and quick SmartGuard to patient association.
SmartGuard® Reader
Several SmartGuard reader make and model numbers can be utilized, depending on the facility’s Device Driver Interface (DDI) requirements. Host interface is USB. Please contact your NeurOptics representative, or Customer Service for additional information (866-99-PUPIL).
Device Driver
The NPi Pupillometer is a point-of-care standalone device which is EMR-enabled but reliant on a driver interface to the hospital EMR system. Please contact your EMR or middleware provider to obtain the appropriate driver or software plug-in for the NeurOptics Pupillometer. If your EMR service provider has not already written the Pupillometer interface, NeurOptics will provide the necessary data protocols upon request.
Workflow

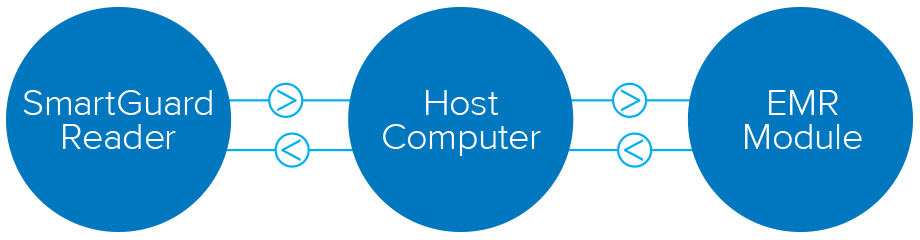
The main EMR application runs in the background of the EMR module or computer and it can access and read data in the SmartGuard memory using the SmartGuard Reader and the associated driver for software interface. Data is then sent to the host computer using standard protocols (ie: HL7). The application in the host computer updates the EMR system with the uploaded information received from the EMR module.
Installation Preparation
To prepare for the installation of the new technology into the clinical environment, please provide your NeurOptics representative with a non-confidential patient ID wristband which will allow us to validate and verify barcode data structure compatibility.